GMA-8003
Murine Anti- Factor VIII
Clone GMA-8003
Background
Factor VIII (FVIII) is a heterodimer consisting of a heavy chain (ranging in mass from 90 to 200 kDa) bound via metal ions to a light chain (80 kDa). In plasma, FVIII circulates in an inactive form bound to von Willebrand factor. Following activation by factor Xa or thrombin, factor VIIIa can function as cofactor for the enzyme factor IXa in the activation of factor X in the presence of phospholipid and Ca2+. Absent or defective FVIII is the cause of the X-linked recessive bleeding disorder hemophilia A. GMA-8003 (also known as 2-117)1 recognizes the C2 domain of FVIII and is suitable for ELISA, bio-layer interferometry pairing, and surface plasmon resonance studies.2
More Information:
Product Datasheet, pdfDescription
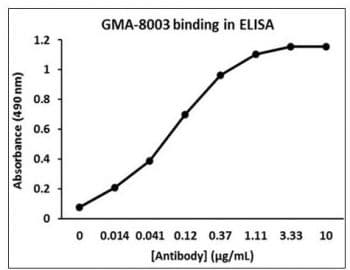
Application
Data:
Purchase GMA-8003
Antibody References:
- S. Meeks et al. (2007). Blood. 110(13):4234-4242.
- P.T. Nguyen et al. (2014). Blood. 123(17):2732-2739.
- R. Summers et al. (2011). Blood. 117(11):3190-8.
- G.S. Pandey et al. (2013). Nat Med. 19(10):1318–1324.
- H. Wakabayashi et al. (2014). The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 289(20):14020–14029.
- H. Wakabayashi, P.J. Fay. (2013). The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 288(43):31289–31297.
- H. Wakabayashi, P.J. Fay. (2013). Biochemistry. 52(22):3921–3929.
- H. Wakabayashi, P.J. Fay. (2013). Biochem J. 452(2):293–301.
- M. Takeyama et al. (2013). Thromb Haemost. 109(2):187–198.
- H. Wakabayashi et al. (2011). The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 286(29):25748 –25755.
