The most commonly employed screening method at Green Mountain Antibodies involves ELISA assay development. ELISA assays are most commonly used for:
-determining mouse or rat serum antibody concentrations
-detecting and measuring antigens in a variety of tissues and samples
-identifying hybridomas producing antigen-specific antibodies
-measuring idiotype-anti-idiotype interactions
ELISA assay development requires selection of a format, developing the best antibodies or critical reagents for that format, and optimizing how the components work together. The screening protocol can then be shared with the customer.
GMAb provides antibodies and working assays for diagnostic use, PD, PK and ADA assays. These critical reagents and assays support our therapeutic customers through pre-clinical and clinical trials.
As a monoclonal antibody and assay development service provider, Green Mountain Antibodies’ goal is to support our customers by developing the best antibodies for their end application. This means our scientists will develop appropriate screening strategies and a Project Plan based on information obtained about the target, available reagents, and how the antibodies will be used in the final assay format. Most often, an ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) assay is used to detect or quantify specific proteins will be the end goal.
Types of ELISA Assay Development employed:
- Indirect ELISA: A standard ELISA method used for screening test bleeds and hybridoma cell lines. Antigen is immobilized onto 96-well plates. Antibody-antigen binding is detected using a secondary antibody conjugated to an enzyme and a chromogenic substrate.
- Capture ELISA: A secondary antibody (for example, goat anti-mouse) is used to capture murine antibodies on a 96 well plate. Avidin-peroxidase and a chromogenic substrate detect bound biotin-labeled antigen.
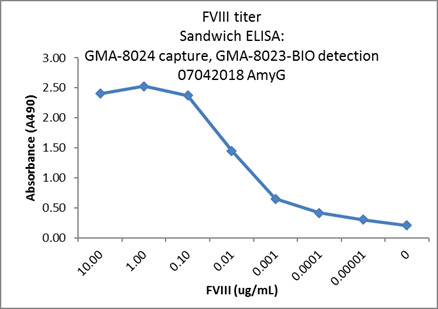
- Matched Pair Sandwich ELISA: The antigen is sandwiched between two primary antibodies, known as the capture and detector antibodies. A labeled secondary antibody is then detected by the antigen. We can also use biolayer interferometry to test matched pairs.
- Competitive ELISA: Using a labeled protein antigen, single monoclonal antibodies are absorbed onto plastic wells. These monoclonal antibodies will bind biotin-labeled protein antigen. Avidin-peroxidase are used to determine Antigen-antibody complexes. Inhibition of biotin-protein by unlabeled protein forms the basis for a standard curve for protein quantification.
- Solution-phase immunoassays: Soluble protein antigens can be quantified in solution by direct measurement of free antibody at equilibrium.
Additional ways that Green Mountain Antibodies is able to characterize your final antibody include affinity ranking by biolayer interferometry, variable region DNA sequencing, IEF, SDS-PAGE, SEC, and dynamic light scattering.
Additional Services