Antibody characterization helps determine the physicochemical and immunochemical properties, biological activity, purity, impurities and quantity of a monoclonal antibody. Characterization is integral to the development of successful assays. GMAb’s capabilities allow for successful antibody characterization of your unique project.
Antibody Labeling with Biotin and Fluorescent Labels
>Antibody Characterization Services
Labeled antibodies are widely used in different assays. Although labeling methods are often kit-based and simple to perform, your time is better spent running experiments, not preparing reagents. Labeling antibodies with biotin and fluorophores are two common modifications offered by Green Mountain Antibodies.
Applications
- Labeled antibody for sandwich ELISA, immunofluorescence, FACS or bead-based assays
- Increase assay sensitivity and decrease background
- Signal amplification in ELISA and Western Blots
- Screening hybridomas when antigen is limited
Explore More Services
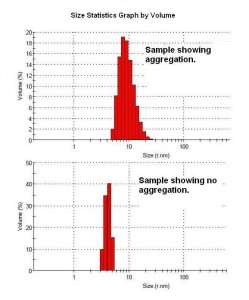
Aggregation Analysis Using SEC and/or Light Scattering
>Antibody Characterization Services
Light scattering is a rapid non-destructive method for studying motions of macromolecules in solution and cells in suspension. Dynamic light scattering measures the diffusion and size of proteins such as monoclonal antibodies, while static light scattering reports the molecular weight and radius of gyration. Knowing that a purified antibody is in solution following purification, can eliminate one more problem variable in understanding why a particular antibody doesn’t work in a particular assay. If the antibody does aggregate, light scattering is a tool for determining alternative solution conditions to improve its behavior in solution. SEC is a method of separating molecules by their size. This provides a reading of the antibody fragments and/or aggregates versus the intact antibody.
Applications
- Detect antibody aggregation or precipitation
- Indication of antibody heterogeneity
*NEW* Gator Analysis
>Antibody Characterization Services
Green Mountain Antibodies has updated our BLI system to the more flexible and highly sensitive Gator Plus. Similar to Octet, the Gator biosensors come in a variety of surface chemistries useful for designing an assay to suit a project’s unique analytical requirements. The new system provides a higher throughput solution that aids GMAb in meeting our customers’ quantitation needs with high levels of accuracy and specificity in crude matrices.
Octet Analysis
>Antibody Characterization Services
The Octet analysis system by ForteBio uses Bio-Layer Interferometry (BLI), a label-free method for measuring bi-molecular interactions. With Dip and Read technology there is no need to purify antibodies to get valuable antigen binding and specificity information. GMAb offers Koff ranking and matched pair data from your select antibodies.
Antibody Sequencing
>Antibody Characterization Services
All antibodies have the same basic protein structure but exhibit sequence variability in those regions that contact the antigen. These so-called “variable regions” represent an approximately 100 amino acid domain found at the amino terminals of both the light and heavy chains of IgG. Different monoclonal antibodies to the same antigen target can also have different variable region sequences. GMAb provides the antibody sequence to allow safety in case the clone is lost, or the end goal is a recombinant antibody.
Fragmentation: Preparation of Fab and F(ab’)2
>Antibody Characterization Services
Sometimes experimental protocols require smaller fragments of IgG. We often see customers use fragmented monoclonal antibodies as immunogens. Two commonly prepared fragments are monovalent Fab, following papain digestion, and bivalent F(ab’)2 from digestion with pepsin. As with all proteolytic reactions, individual antibodies can have different susceptibility to different proteases. Consequently, we recommend a pilot digestion using standard conditions before scale up.
- Fab and Fc: Incubation with papain results in cleavage of immunoglobulin at the hinge region. Further purification on Protein A-agarose separates the antigen binding Fab from the Fc region. Fragments can be further purified and analyzed using exclusion chromatography.
- F(ab’)2 : Cleavage with pepsin produces one F(ab’)2 fragment and smaller Fc portions. These fragments are useful for conjugation with detectable labels as the sulfhydryl group is still intact.
Advantages
- Eliminates binding to Fc receptors
- Improved staining in immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- Easier penetration of tissues
- More useful in some applications when 150 kD proves too large
